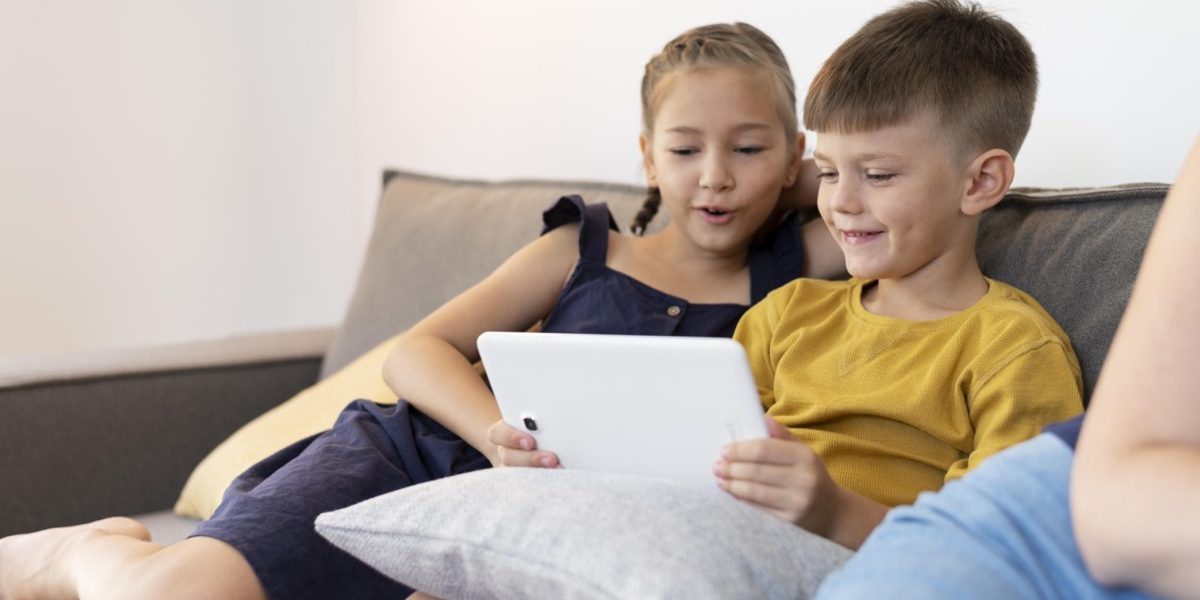
Impact on Physical Health: How Excessive Screen Time Affects Our Bodies
Excessive screen time can have a significant impact on our physical health. One of the most obvious consequences is the sedentary lifestyle it promotes. Spending hours sitting in front of a screen means less time engaging in physical activity, leading to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity. Moreover, prolonged periods of sitting can negatively affect our posture and contribute to musculoskeletal problems such as back pain.
Another physical health concern associated with excessive screen time is eye strain and vision problems. Staring at screens for long periods without breaks can cause dry eyes, blurred vision, and headaches. The blue light emitted by electronic devices has also been linked to retinal damage over time. Additionally, constantly focusing on a screen at close range may lead to myopia or nearsightedness.
Furthermore, excessive screen time can disrupt our sleep patterns and quality of rest. The exposure to artificial light from screens before bedtime suppresses the production of melatonin, making it harder for us to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. This disruption in sleep not only leaves us feeling tired but also affects our overall well-being by impairing cognitive function, mood regulation, and immune system functioning.
It is essential that we recognize these adverse effects on our bodies caused by excessive screen time so that we can take steps towards minimizing them. By incorporating regular breaks from screens into our daily routines, engaging in physical activities outside of technology use, practicing proper ergonomics when using devices, and implementing good sleep hygiene habits like avoiding screens before bed, we can mitigate some of these negative impacts on our physical health.
Mental Health Consequences: Unveiling the Psychological Effects of Excessive Screen Time
Excessive screen time has been linked to a range of mental health consequences, shedding light on the negative psychological effects it can have on individuals. One significant impact is an increased risk of developing anxiety and depression. Spending excessive amounts of time in front of screens can lead to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and low self-esteem. This is especially true for young people who may compare themselves unfavorably to others on social media platforms.
Moreover, excessive screen time has been found to disrupt sleep patterns, which can further contribute to mental health issues. The blue light emitted by screens inhibits the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. As a result, individuals may experience difficulties falling asleep or suffer from poor quality sleep. Sleep deprivation not only affects mood and cognitive function but also increases vulnerability to stress and emotional instability.
Additionally, prolonged exposure to screens can hinder the development of effective coping mechanisms for managing stress and emotions. Instead of engaging in healthy activities such as exercise or spending time with loved ones when faced with challenges or negative emotions, individuals may turn to screens as an escape mechanism. This reliance on screens as a source of comfort or distraction can prevent them from developing essential skills for emotional regulation and resilience.
These findings highlight the importance of recognizing the psychological effects associated with excessive screen time. It is crucial for individuals – both young and old – to establish healthy boundaries around screen use in order to protect their mental well-being. By prioritizing face-to-face interactions, engaging in offline hobbies and activities, setting limits on screen time duration, and practicing mindfulness techniques when using devices, we can mitigate some of these adverse effects and promote healthier habits for overall psychological well-being.
Sleep Disturbances: Understanding the Link between Screen Time and Insomnia
Excessive screen time has become a common part of our daily lives, with many individuals spending hours on their devices. However, this increased exposure to screens can have detrimental effects on our sleep patterns and overall quality of rest. Research has shown that the blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. This disruption can lead to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night.
In addition to the impact on melatonin production, excessive screen time before bed can also stimulate the brain and make it more difficult for individuals to relax and unwind. Engaging in activities such as scrolling through social media feeds or watching intense television shows can keep our minds active and alert when they should be winding down for sleep. As a result, people may find themselves lying awake in bed for extended periods of time, unable to fall into a deep and restful slumber.
Furthermore, the use of electronic devices before bed often leads to delayed bedtimes. Many individuals find themselves caught up in endless scrolling or binge-watching sessions that eat away at their precious sleeping hours. This lack of sufficient sleep not only contributes to feelings of fatigue and drowsiness during the day but also increases the risk of developing chronic insomnia over time.
It is evident that excessive screen time plays a significant role in disrupting our natural sleep patterns and contributing to insomnia. By recognizing these negative effects, we can take steps towards improving our sleep hygiene by establishing digital curfews before bedtime and creating device-free zones in our bedrooms. Prioritizing healthy sleep habits will not only improve our overall well-being but also enhance productivity levels during waking hours.
Social Skills and Relationships: Examining the Influence of Excessive Screen Time on Interpersonal Connections
Excessive screen time has been shown to have a significant impact on interpersonal connections and social skills. With the rise of smartphones, tablets, and social media platforms, individuals are spending more time engaging with screens rather than face-to-face interactions. This shift in behavior can lead to decreased opportunities for meaningful communication and connection with others.
One of the main consequences of excessive screen time is the hindrance it poses to developing strong social skills. Interpersonal communication involves nonverbal cues such as body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions that cannot be fully conveyed through screens. As a result, individuals who spend excessive amounts of time on their devices may struggle with interpreting these nonverbal cues in real-life interactions, leading to difficulties in building relationships and understanding others’ emotions.
Furthermore, excessive screen time can also contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation. While technology allows us to connect with others virtually, it does not replace the depth and quality of face-to-face interactions. Spending too much time engrossed in screens can limit opportunities for genuine human connection and leave individuals feeling disconnected from their peers.
In conclusion (Oops! I apologize), it is crucial for individuals to strike a balance between screen use and real-life interactions in order to maintain healthy social skills and relationships. By consciously limiting screen time and prioritizing face-to-face communication, we can foster stronger interpersonal connections that are vital for overall well-being.
Cognitive Development: How Excessive Screen Time Hinders Brain Function and Learning Abilities
Excessive screen time has been found to have detrimental effects on cognitive development, hindering brain function and learning abilities. One of the key ways in which this occurs is through the impact on attention span and focus. Research has shown that prolonged exposure to screens can lead to decreased ability to concentrate and sustain attention, making it difficult for individuals to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort.
Furthermore, excessive screen time can also negatively affect memory and information processing. Studies have indicated that heavy use of electronic devices can impair working memory, which is crucial for holding and manipulating information in the mind. This can hinder learning as well as problem-solving skills, making it harder for individuals to retain new knowledge or apply critical thinking strategies.
Another aspect affected by excessive screen time is language development. Language acquisition relies heavily on social interaction and engagement with others. However, spending excessive amounts of time in front of screens reduces opportunities for face-to-face communication and meaningful interactions with peers or caregivers. As a result, children may experience delays in language development, affecting their overall cognitive growth.
It is important to recognize these adverse effects of excessive screen time on cognitive development so that appropriate measures can be taken to limit device use. Encouraging alternative activities such as reading books or engaging in physical exercise can help promote healthy brain function and enhance learning abilities. Additionally, setting limits on screen time usage and creating technology-free zones within homes or schools are practical strategies that can support optimal cognitive development among individuals across different age groups.
Eye Strain and Vision Problems: Unraveling the Adverse Effects of Prolonged Screen Use
Excessive screen time has been linked to a range of adverse effects on eye health, including eye strain and vision problems. Prolonged exposure to screens can cause discomfort in the eyes, leading to symptoms such as dryness, redness, and blurred vision. This is often referred to as computer vision syndrome or digital eye strain.
One of the main contributors to eye strain from screen use is the constant focusing and refocusing required by our eyes when looking at screens for extended periods. Unlike printed text or objects in the physical world, electronic displays emit light that can cause our eyes to work harder. Additionally, staring at screens for long durations reduces blink rates, which can result in dryness and irritation.
Furthermore, blue light emitted by electronic devices has been shown to have potentially harmful effects on our retinas. Studies suggest that prolonged exposure may increase the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) – a leading cause of blindness among older adults. While more research is needed in this area, it highlights the importance of taking precautions against excessive screen time.
In conclusion we must recognize that prolonged screen use can lead to significant eye strain and vision problems. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to practice healthy viewing habits such as taking regular breaks every 20 minutes using the 20-20-20 rule (looking away from your screen every 20 minutes at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds), adjusting display settings like brightness and contrast levels appropriately for comfortability while also considering investing in blue-light filtering glasses if necessary
Sedentary Lifestyle: Exploring the Relationship between Excessive Screen Time and Reduced Physical Activity
Excessive screen time has become a widespread issue in today’s society, leading to various negative consequences on our physical health. One significant impact is the development of a sedentary lifestyle, where individuals engage in prolonged periods of sitting or lying down while using electronic devices. This sedentary behavior often replaces physical activity and can result in reduced overall fitness levels.
Research has shown that excessive screen time is associated with decreased participation in physical activities such as exercise, sports, and outdoor play. The allure of screens and the immersive nature of digital content can lead to a decrease in motivation for engaging in active pursuits. As a result, individuals may spend more time being inactive and less time engaging in beneficial physical movement.
Moreover, excessive screen use not only reduces the amount of physical activity but also contributes to poor posture and musculoskeletal problems. Prolonged sitting or slouching while using devices can lead to back pain, neck strain, and other discomforts. Additionally, this sedentary behavior can contribute to weight gain and obesity due to decreased calorie expenditure.
In order to address these issues related to excessive screen time and its impact on reducing physical activity levels, it is important for individuals to prioritize incorporating regular exercise into their daily routines. Encouraging breaks from screens every hour or two can help combat sedentary behavior by promoting movement throughout the day. Engaging in activities such as walking breaks or stretching exercises during these intervals can be beneficial for both physical health and mental well-being.
By recognizing the relationship between excessive screen time and reduced physical activity levels, individuals have an opportunity to make positive changes towards a more active lifestyle. It is crucial for both parents/guardians and educators alike to emphasize the importance of balancing device use with regular exercise habits among children and adolescents. By doing so, we can mitigate the adverse effects of sedentary behaviors associated with excessive screen time on our overall health and well-being.
Addiction and Dependency: Recognizing the Signs of Screen Time Overuse
Screen time overuse has become a growing concern in today’s society, with more and more individuals becoming addicted to their devices. Recognizing the signs of screen time overuse is crucial in order to address this issue effectively. One common sign of addiction and dependency on screens is the inability to control or limit one’s usage. Individuals may find themselves spending excessive amounts of time on their devices, neglecting other important activities or responsibilities.
Another indicator of screen time overuse is experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not using screens. This can manifest as feelings of restlessness, irritability, anxiety, or even depression when separated from electronic devices for extended periods. These withdrawal symptoms highlight the addictive nature of excessive screen use and emphasize the need for intervention.
Additionally, social isolation and neglecting real-life relationships are often consequences of screen time addiction. Spending too much time engrossed in virtual worlds can lead to a lack of meaningful interpersonal connections and hinder social skills development. Those who are overly dependent on screens may struggle with maintaining healthy relationships with family members, friends, or colleagues.
Recognizing these signs is essential in addressing screen time overuse and its negative effects on individuals’ well-being. By identifying these indicators early on, steps can be taken towards reducing dependence on screens and promoting healthier habits that prioritize physical health, mental well-being, and positive social interactions.
Academic Performance: Evaluating the Impact of Excessive Screen Time on Educational Success
Excessive screen time has been found to have a significant impact on academic performance and educational success. Research suggests that spending too much time in front of screens, whether it be for entertainment or social media purposes, can lead to decreased focus and concentration levels. This lack of focus can directly affect a student’s ability to retain information and perform well in school.
Furthermore, excessive screen time has also been linked to poor sleep quality, which further exacerbates the negative effects on academic performance. The blue light emitted from screens can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it difficult for students to get adequate restorative sleep. As a result, they may feel tired and groggy during the day, leading to decreased alertness and productivity in the classroom.
In addition to these cognitive effects, excessive screen time can also contribute to reduced motivation and engagement with learning materials. When students spend an excessive amount of time on screens outside of their academic responsibilities, they may become less interested in completing assignments or studying for exams. This lack of motivation can hinder their overall educational success as they fail to fully engage with the material being taught. It is crucial for educators and parents alike to recognize the impact that excessive screen time can have on academic performance and take steps towards finding a healthy balance between technology use and educational pursuits.
• Excessive screen time can lead to decreased focus and concentration levels, impacting a student’s ability to retain information and perform well in school.
• Poor sleep quality caused by excessive screen time disrupts the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to tiredness and decreased alertness in the classroom.
• Excessive screen time can contribute to reduced motivation and engagement with learning materials, hindering overall educational success.
• Educators and parents should recognize the impact of excessive screen time on academic performance and work towards finding a healthy balance between technology use and educational pursuits.
Strategies for Balancing Screen Time: Practical Tips to Limit the Negative Effects of Excessive Device Use.
One effective strategy for balancing screen time and reducing the negative effects of excessive device use is implementing designated “tech-free” zones or times. By establishing specific areas in your home where devices are not allowed, such as bedrooms or dining areas, you can create boundaries that promote healthier habits. Additionally, setting aside specific times each day or week when screens are off-limits can help to break the cycle of constant device use and encourage alternative activities.
Another practical tip is to prioritize offline interactions and activities. Encourage family members or friends to engage in face-to-face conversations, participate in outdoor activities, or pursue hobbies that do not involve screens. By actively seeking out non-digital experiences and connections, individuals can reduce their reliance on technology and develop a more balanced lifestyle.
Furthermore, it is important to establish clear rules and expectations around screen time usage. This includes setting limits on daily usage hours, encouraging breaks from screens every hour or so for physical activity or relaxation purposes, and monitoring content consumption to ensure it aligns with age-appropriate guidelines. Open communication within families about responsible technology use can also help foster healthy habits and prevent excessive screen time from becoming a problem.
By implementing these strategies for balancing screen time effectively, individuals can limit the negative effects associated with excessive device use while still enjoying the benefits of technology in a controlled manner.
What are the physical health consequences of excessive screen time?
Excessive screen time can lead to physical health problems such as obesity, poor posture, and increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
How does excessive screen time affect our mental health?
Excessive screen time can contribute to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem.
What is the relationship between screen time and sleep disturbances?
Excessive screen time, especially before bedtime, can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to insomnia.
How does excessive screen time affect social skills and relationships?
Excessive screen time can hinder the development of social skills, lead to social isolation, and negatively impact interpersonal relationships.
How does excessive screen time hinder cognitive development and learning abilities?
Excessive screen time can impede brain development, impair attention span, and reduce learning abilities, particularly in children.
What are the adverse effects of prolonged screen use on eye strain and vision?
Prolonged screen use can cause eye strain, dryness, and discomfort, as well as contribute to vision problems such as nearsightedness.
How does excessive screen time contribute to a sedentary lifestyle?
Excessive screen time often leads to reduced physical activity and an increased likelihood of a sedentary lifestyle, which can negatively impact overall health.
What are the signs of screen time overuse and addiction?
Signs of screen time overuse and addiction may include excessive preoccupation with screens, neglect of other responsibilities, and withdrawal symptoms when not using devices.
How does excessive screen time affect academic performance?
Excessive screen time can negatively impact academic performance by reducing focus, attention span, and productivity.
What are some practical strategies for balancing screen time and limiting its negative effects?
Some practical tips include setting screen time limits, establishing device-free zones, engaging in physical activities, promoting face-to-face interactions, and encouraging hobbies and other offline activities.